In the healthcare industry, the quality of patient care depends on the competence of the providers delivering it. Medical credentialing is a crucial process that verifies the qualifications, experience, and expertise of healthcare providers to ensure they are qualified to offer high-quality care. This process not only maintains standards but also builds trust between patients and healthcare organizations, reinforcing the reliability of medical institutions. Let’s dive into what medical credentialing entails, why it matters, and how it impacts the healthcare landscape.
What is Medical Credentialing?
Medical credentialing is the process of verifying a healthcare provider’s qualifications, including their education, training, experience, and professional licenses. Credentialing ensures that doctors, nurses, and other medical practitioners meet the standards required to practice within a healthcare facility or organization. This verification process is extensive, requiring primary source verification from licensing boards, academic institutions, and certification bodies.
The credentialing process is typically managed by a credentialing department within healthcare organizations or by third-party agencies specializing in credentialing services.
The Key Steps in the Medical Credentialing Process
Medical credentialing involves several key steps to thoroughly assess and verify a provider’s qualifications. Here’s an overview of the steps involved:
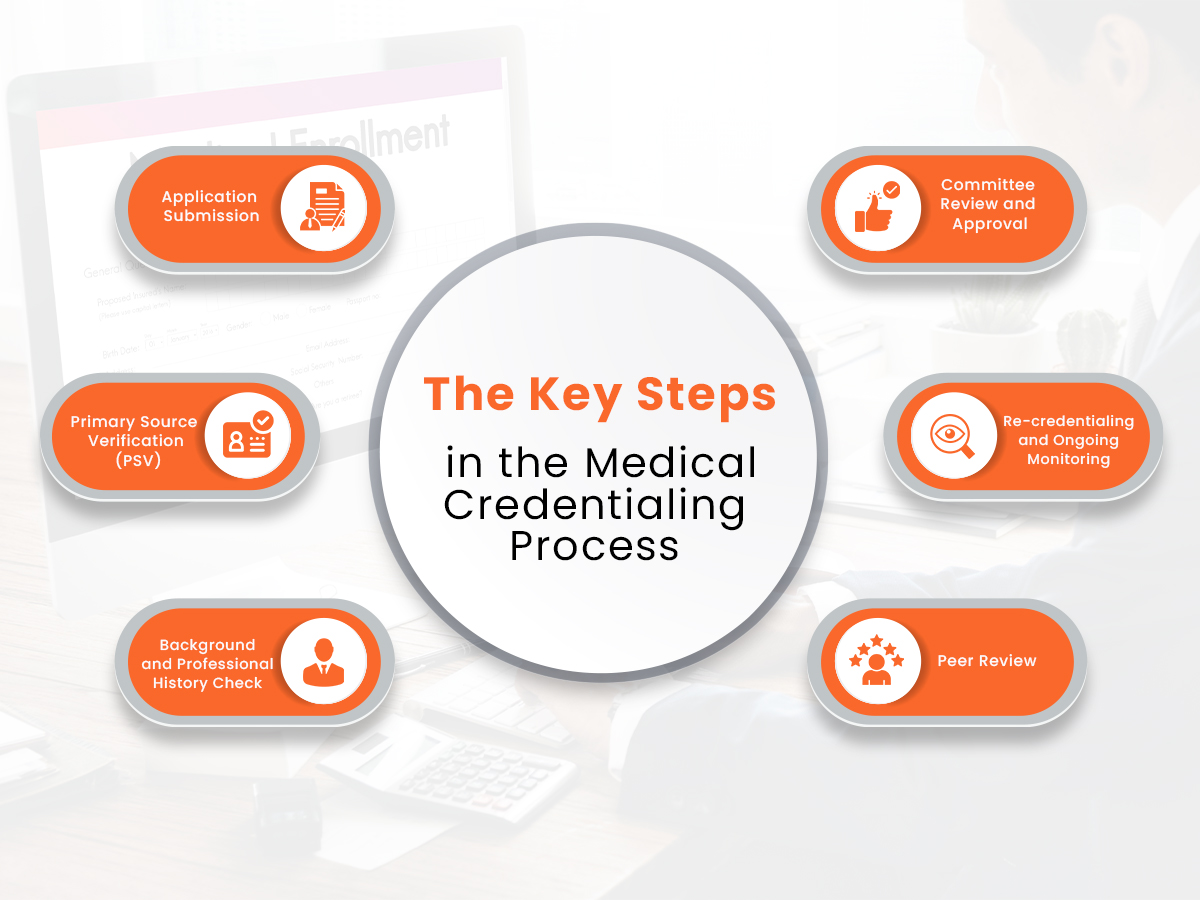
- Application Submission
Providers submit an application detailing their educational background, training, certifications, work experience, and licensing. This application serves as the foundation for the credentialing process. - Primary Source Verification (PSV)
Credentialing requires primary source verification, where the information provided by the healthcare provider is directly confirmed with original sources. This could involve contacting universities for transcripts, licensing boards for certifications, and previous employers for work experience. - Background and Professional History Check
Credentialing often includes a background check to review criminal history, malpractice claims, or disciplinary actions, if any. This step ensures the provider has a record of professional conduct. - Peer Review
A peer review may be conducted to obtain insights into the provider’s professional behavior, ethical standards, and competence from other practitioners who have worked with them. - Committee Review and Approval
Once the credentialing specialist compiles the information, a credentialing committee reviews the application. This committee, typically consisting of healthcare administrators and senior clinicians, makes the final decision on whether the provider is approved to practice. - Re-credentialing and Ongoing Monitoring
Credentialing is not a one-time process. Healthcare providers undergo re-credentialing periodically, ensuring they continue to meet current standards, renew their licenses, and complete ongoing education.
Why is Medical Credentialing Important?
Medical credentialing is fundamental to patient safety, regulatory compliance, and maintaining the quality of healthcare services. Here’s why it matters:
- Patient Safety and Trust
By verifying the qualifications of providers, credentialing safeguards patients from unqualified or underqualified professionals. Patients can trust that they are receiving care from competent, skilled providers, which is essential in building a trustworthy healthcare system. - Regulatory Compliance
Healthcare is a highly regulated industry, with government and state agencies requiring hospitals and clinics to meet strict standards. Medical credentialing ensures that organizations comply with these regulations, reducing the risk of penalties, lawsuits, and reputational harm. - Quality Assurance
Credentialing contributes to quality control in healthcare by ensuring that only providers who meet industry standards and possess the required expertise are allowed to practice. This supports the overall goal of delivering safe, high-quality care to patients. - Financial Impact
Credentialing also affects reimbursement from insurance companies and government payers, such as Medicare and Medicaid. Insurers often require that providers are credentialed to process claims, making credentialing financially important for healthcare institutions.
Challenges in Medical Credentialing
The credentialing process, while necessary, can be challenging due to its complexity and the high volume of data involved. Some common challenges include:
- Time-Consuming Process
The process of verifying credentials with various institutions can be lengthy, often taking weeks or even months, which can delay onboarding for healthcare providers. - Data Management
With hundreds of healthcare providers in large institutions, managing credentialing data can be overwhelming. Accurate data management is critical, as any errors can lead to compliance issues and potential risks. - Changing Regulations
Healthcare regulations and credentialing requirements are frequently updated, requiring credentialing departments to stay informed and adapt their processes accordingly. - Administrative Burden
Managing credentialing applications, background checks, and peer reviews is a labor-intensive process that requires dedicated staff, increasing the administrative workload for healthcare organizations.
The Role of Technology in Medical Credentialing
With advancements in technology, many organizations are turning to digital solutions to streamline the credentialing process. Credentialing software and platforms automate data collection, verification, and compliance checks, reducing administrative burdens and improving efficiency. Here are some ways technology is transforming credentialing:
- Automated Verification
Credentialing software can automate primary source verification, saving time and reducing errors associated with manual verification. - Centralized Data Management
Digital platforms allow credentialing departments to centralize provider data, making it easier to manage records, monitor renewal deadlines, and maintain an accurate, accessible database. - Compliance Tracking
Credentialing software can monitor regulatory changes and notify administrators of upcoming re-credentialing requirements, helping organizations stay compliant. - Real-Time Reporting and Analytics
Analytics features in credentialing software provide insights into the status of credentialing processes, helping organizations identify bottlenecks and optimize efficiency.
Becoming a Credentialed Healthcare Provider
For healthcare providers, understanding the credentialing process is crucial. It’s a standard requirement for most healthcare jobs, and knowing the requirements in advance can streamline the process. Providers should be prepared to submit their diplomas, certificates, licenses, work experience, and other documentation accurately and promptly. Providers can also benefit from credentialing software that allows them to track their application status and receive reminders for re-credentialing deadlines.
Conclusion
Medical credentialing plays an indispensable role in upholding the standards of healthcare, protecting patients, and ensuring compliance. As healthcare regulations evolve, and as the need for qualified providers grows, the importance of efficient, effective credentialing processes will only increase. With the integration of technology, the future of credentialing is set to become more streamlined, making it easier for healthcare organizations to maintain high standards of care.
Through medical credentialing, healthcare organizations not only meet regulatory requirements but also reaffirm their commitment to delivering safe, quality care. For providers, it’s an assurance that they are joining a profession built on trust, skill, and excellence.





