
In the fast-paced and ever-evolving world of healthcare, licensing plays a pivotal role in ensuring the safety and quality of patient care. Proper licensing not only validates the qualifications and expertise of healthcare professionals but also serves as a crucial regulatory mechanism. In the context o
f Behavioral Health and Mental Health Providers, licensure becomes even more paramount as it directly impacts the well-being and mental health support of individuals seeking assistance. Understanding the significance of licensing in this specialized field is essential for both providers and the communities they serve.
Understanding the Basics of Licensing for Healthcare Providers
Licensing serves as a formal validation of a provider’s qualifications, education, and professional competency, instilling confidence in patients seeking behavioral and mental health services. It acts as a vital safeguard, ensuring that those offering these specialized services have met the necessary standards and adhere to ethical guidelines.
The process of obtaining a license for Behavioral Health and Mental Health Providers typically involves completing accredited education programs, acquiring relevant clinical experience, and passing rigorous exams. Licensing boards, often governed by state or national regulatory bodies, oversee the issuance and renewal of licenses, ensuring that providers remain up-to-date with the latest developments in their fields through continuing education requirements.
While licensing ensures a certain level of standardization, it is essential to acknowledge the diversity and complexity within the Behavioral Health and Mental Health fields. Different areas, such as counseling, psychology, social work, or psychiatry, may have distinct licensing requirements. Moreover, licensing regulations may vary from one state or country to another, leading to potential challenges for providers who wish to practice across borders.
What is Traditional (Normal) Licensing Process?
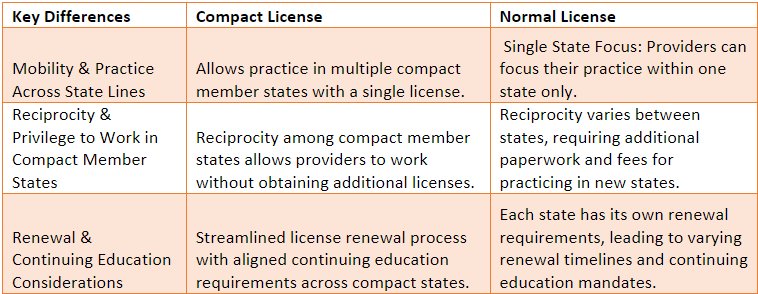
The Traditional (Normal) Licensing Process refers to the standard procedure through which healthcare professionals, including Behavioral Health and Mental Health Providers, obtain their licenses. It involves completing state-specific education, clinical experience, and examination requirements, ensuring their qualifications meet the necessary standards to practice within a particular state’s jurisdiction.
What is Compact License Option?
The Compact License Option, also known as the Nurse Licensure Compact (NLC), extends to Behavioral Health and Mental Health Providers, allowing qualified professionals to practice across state lines with a single multistate license. It streamlines the licensing process, promoting telehealth opportunities and enhancing access to care, particularly in areas facing provider shortages.
Key Differences Between Compact and Normal Licenses
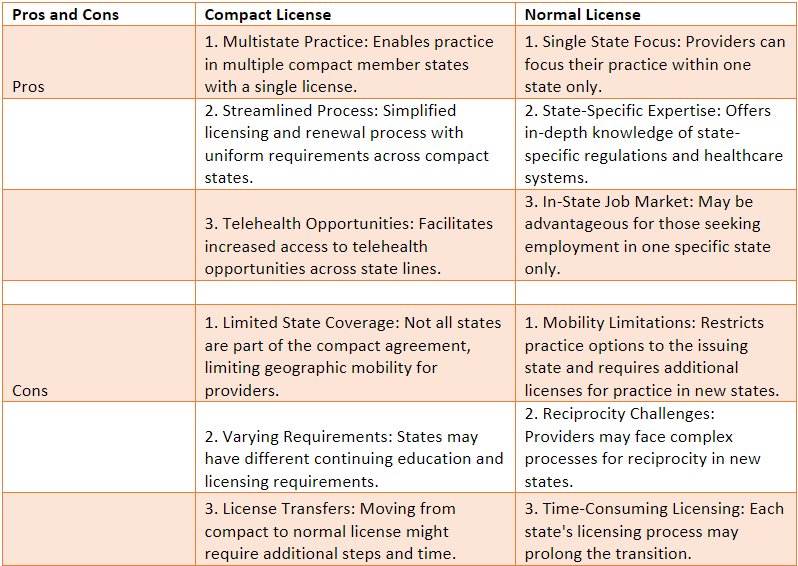
Pros and Cons of Compact and Normal Licenses
Best Practices for Providers Seeking Licensure in Different States
By following these best practices, providers can position themselves for success in obtaining licensure in different states.
- Evaluating the Mobility Needs of the Provider:
- Assess mobility needs and career aspirations before seeking licensure in different states.
- Consider factors like willingness to relocate, desire for telehealth opportunities, and potential job market expansion.
- Make informed decisions on whether to opt for a Compact License or individual licenses based on state preferences.
- Understanding State-Specific Requirements and Variations:
- Research and understand state-specific requirements and regulations for licensing behavioral health and mental health providers.
- Thoroughly study the licensing process, educational prerequisites, and clinical experience mandates of each desired state.
- Being well-informed about state-specific variations ensures a smoother and more efficient licensure application process.
- Maintaining Compliance with Licensing Regulations:
- Stay updated with licensing regulations and keep licenses current for providers seeking practice in different states.
- Comply with continuing education requirements, timely renewals, and any other stipulations imposed by licensing boards.
- Failure to maintain compliance may lead to challenges in practicing across state lines or penalties that hinder professional growth.
The Future of Licensing for Behavioral Health and Mental Health Providers
The future of licensing for Behavioral Health and Mental Health Providers holds promising opportunities for enhanced access through telehealth advancements, potential national licensing standards, and interdisciplinary collaboration. Ongoing professional development, addressing workforce shortages, and managing ethical and legal implications of telehealth will be critical. Advancements in licensure technology are expected to streamline the process, ensuring optimal patient care, and supporting the evolving needs of the mental health workforce.
In conclusion, licensing plays a vital role in the healthcare industry, particularly for Behavioral Health and Mental Health Providers. Understanding the differences between Compact and Normal Licenses, as well as the best practices for licensure in different states, empowers providers to make informed decisions and offer quality care. As the future of licensing unfolds, embracing telehealth advancements, standardized standards, and continued professional development will shape a more accessible and integrated mental health landscape. APAANA Healthcare is committed to supporting providers in navigating the licensing process. Our services are designed to support Behavioral Health and Mental Health Providers in securing the right licenses and advancing their careers with confidence. Take the next step toward a successful future in mental healthcare with APAANA Healthcare.
References
- National Council of State Boards of Nursing (NCSBN) – https://www.ncsbn.org/
- American Psychological Association (APA) – https://www.apa.org/
- National Association of Social Workers (NASW) – https://www.socialworkers.org/ trends in different states.
- American Psychiatric Association (APA) – https://www.psychiatry.org/ requirements.
- American Counseling Association (ACA) – https://www.counseling.org/
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) – https://www.hhs.gov/





